A little deeper
How to find the equation without time.
The equations of motion for constant acceleration are mixtures of the variables in play:
- space
- time
- velocity
- acceleration
We started with space and time and by letting Galileo motivate our choices produced:
Notice that I used “” here which is meant to apply to horizontal acceleration (like walking or in your car) or a vertical direction (like dropping something or throwing something up). This is the most general as it allows for a situation in which the initial position is not 0 and in which the initial velocity is not 0. For example, we could be standing on a roof (at a value of that might be 100 feet) and not just drop something, but throw it straight down so that the initial velocity might be 50 mph.
But we can derive this from some simple definitions.
Remember that the average speed is equal to:
Let’s remember what the areas mean for velocity. Suppose we have a constant velocity, then the initial velocity is equal to the final velocity and is obviously equal to the average velocity: . By rearranging Equation \@ref(eq:avev):
We see that this has the form of an area equation, and the figure suggests that the area under a curve of velocity versus time is the distance traveled:
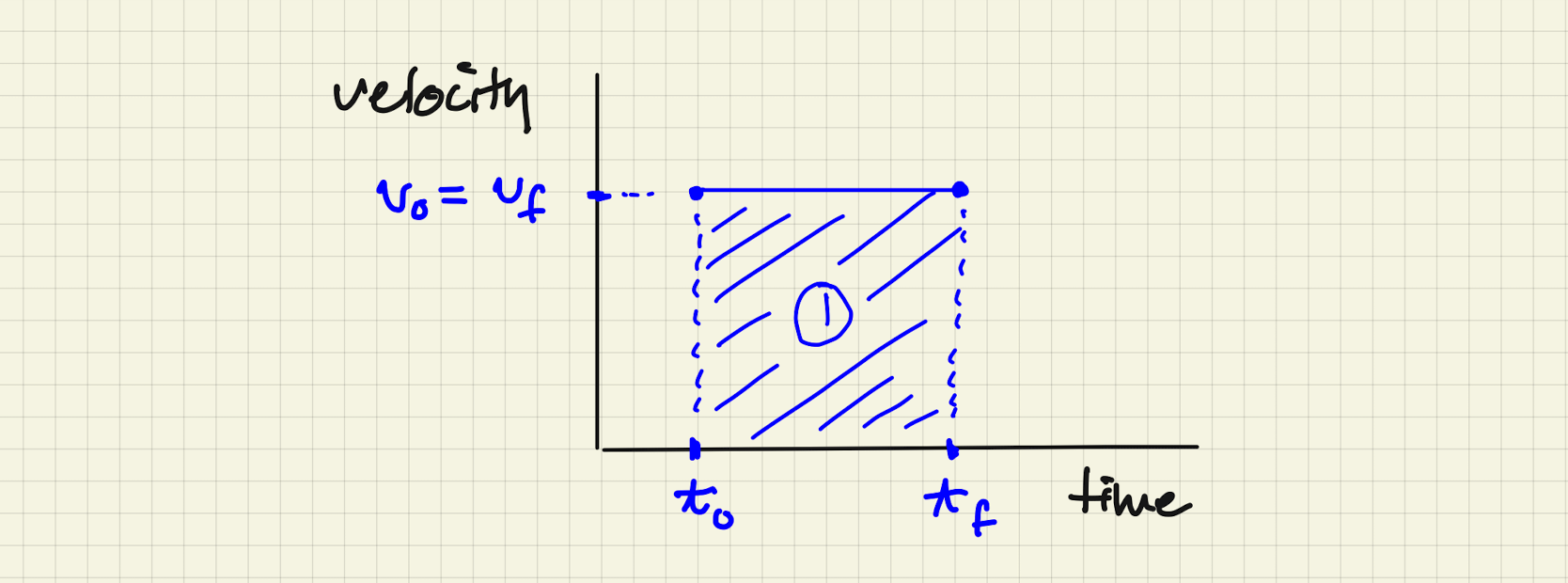 Constant velocity.
Constant velocity.
So let’s call to be the area in the figure.
This is general: the distance traveled is the area under the curve of the velocity as a function of time.
Average velocity for constant acceleration
Let’s step it up to a constant acceleration, which means that the velocity will increase linearly as a function of time. Here it is:
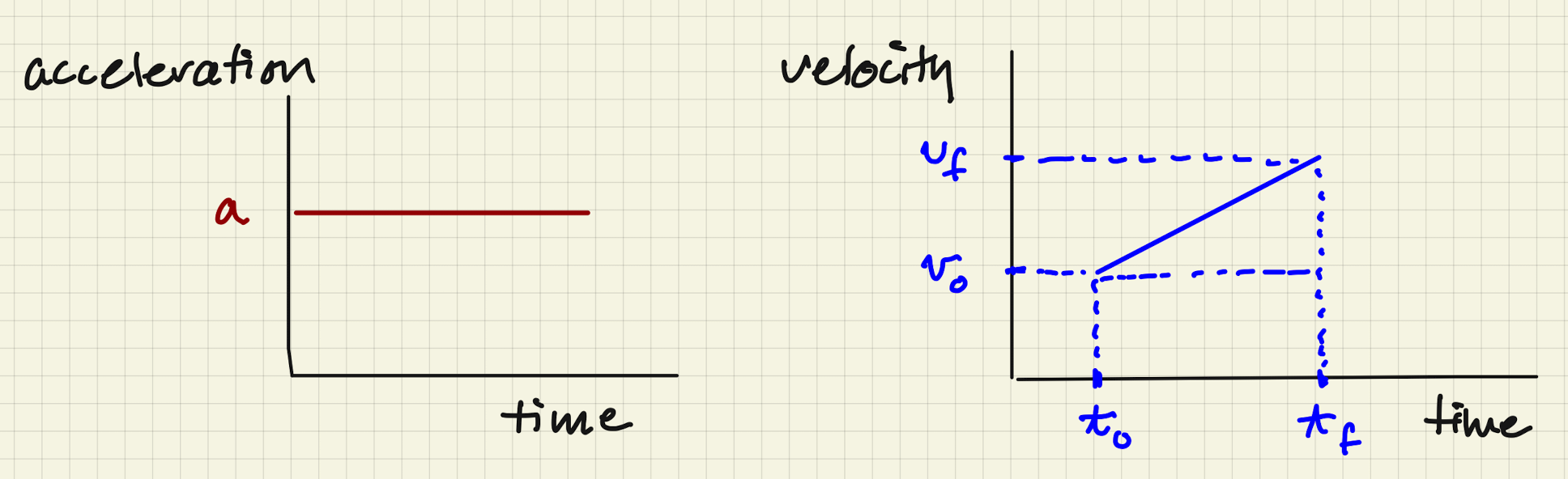 On the left: Acceleration for a...um…constant acceleration. On the right: Velocity for a constant acceleration.
On the left: Acceleration for a...um…constant acceleration. On the right: Velocity for a constant acceleration.
Now what’s the average velocity? Well, we calculate the area under the ramped velocity curve and divide by the time and that’s the average velocity as in Equation \@ref(eq:avev2). Here it is, using the new area definitions in the figure.
That’s interesting. If I’m 6 feet tall and you’re 5 feet tall, what’s the average of our two heights? That’s simple:
We’ve just seen that for a constant acceleration (only) the average velocity is just the average of the beginning and ending velocities:
Don’t buy it? Look at this geometrical construction.
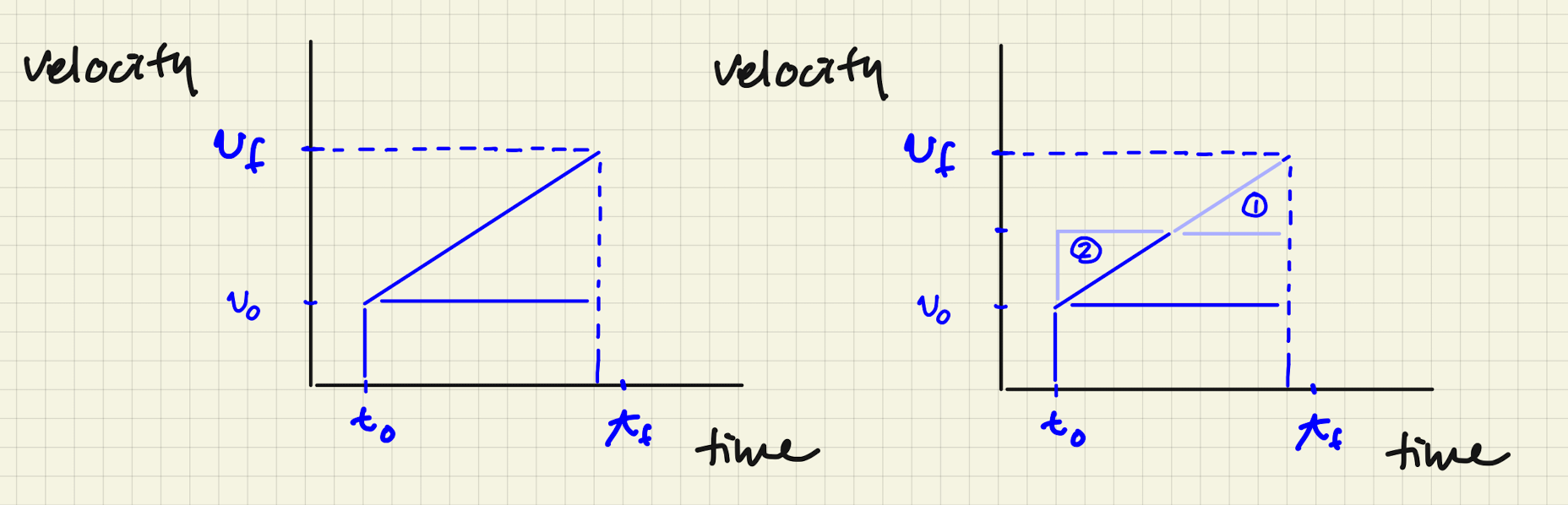 On the left: the same straight velocity curve (line) for constant acceleration as above. In the middle, remove the upper corner triangle at the midpoint. On the right: Moving things around to replace that triangle in the slot to the left.
On the left: the same straight velocity curve (line) for constant acceleration as above. In the middle, remove the upper corner triangle at the midpoint. On the right: Moving things around to replace that triangle in the slot to the left.
We started in the left at an initial speed of at and then at constant acceleration, go faster by time to . Let’s calculate the areas differently:
- Lop off the little notch at the top of the triangle. You can see it is gone in the middle figure, with only a shadow of it remaining. So . So the area is less overall.
- Now restore that in the little area to the left of the truncated triangle.
- Now we have a rectangle .
- The area that we started with is now the same as in the right-hand figure, but it’s now the sum of the areas of two rectangles:
But what’s ? In order for this construction to work, has to be the midpoint between and :
So here we go:
and we get the same result as above:
Now, with this result for the average velocity, we can derive the rest of the equations in the chapter.
The first equation
The total displacement, is still the area under the velocity curve and the average velocity is still
The second equation
Likewise, the average acceleration is:
The third equation
If we now try to isolate and , we can derive the third equation of the set. Let’s take our constant acceleration average velocity and substitute into it Equation \@ref(eq:second):
Now go to Equation \@ref(eq:firstagain) and substitute from this:
Now if we remember that and that we can always force , we get
The fourth equation
Now we can eliminate time and get the fourth equation.
If we substitute this into Equation \@ref(eq:thirdagain) we get:
Now after a tedious algebra event… we get the fourth equation:
Whew.